A conserved regulatory logic controls temporal identity in mouse neural progenitors. Mattar P, Ericson J, Blackshaw S, Cayouette M. Neuron. 2015 Feb 4;85(3):497-504.
Scientific impact: In this article, we show that the zinc finger transcription factor Casz1 controls temporal identity of retinal progenitors during development. We report that Casz1 is essential for the production of neurons at the appropriate stage of development, such as cones during early stages and rods during late stages. This is the first demonstration of a role for Casz1 in the retina, opening the door to novel cell therapy approaches.
* * *
Original abstract
Neural progenitors alter their output over time to generate different types of neurons and glia in specific chronological sequences, but this process remains poorly understood in vertebrates. Here we show that Casz1, the vertebrate ortholog of the Drosophila temporal identity factor castor, controls the production of mid-/late-born neurons in the murine retina. Casz1 is expressed from mid/late stages in retinal progenitor cells (RPCs), and conditional deletion of Casz1 increases production of early-born retinal neurons at the expense of later-born fates, whereas precocious misexpression of Casz1 has the opposite effect. In both cases, cell proliferation is unaffected, indicating that Casz1 does not control the timing of cell birth but instead biases RPC output directly. Just as Drosophila castor lies downstream of the early temporal identity factor hunchback, we find that the hunchback ortholog Ikzf1 represses Casz1. These results uncover a conserved strategy regulating temporal identity transitions from flies to mammals.
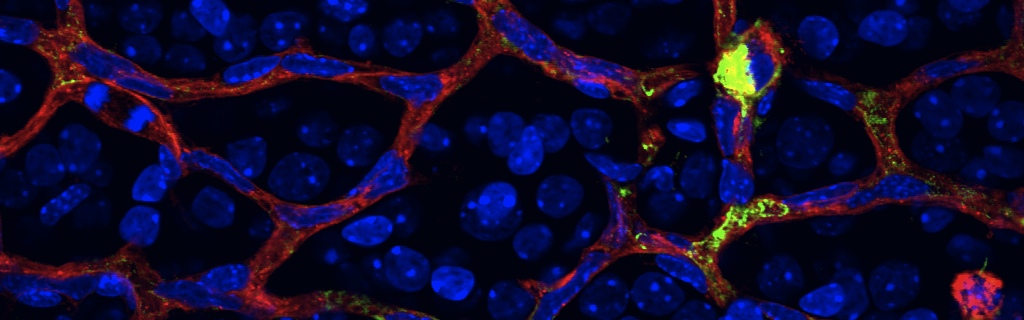
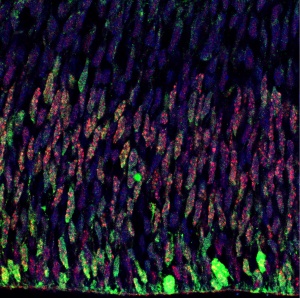
Casz1 expression (red) in retinal progenitors (green) at embryonic day 18